Decentralized social networks are rapidly evolving, and two protocols have emerged at the forefront: Farcaster and Lens Protocol. Both aim to return control of identity and content to users, but for developers seeking to build on these platforms, the devil is in the details. Understanding their differences is crucial for making an informed choice when architecting your next Web3 social application.

Technical Architecture: Layered vs. Tokenized Approaches
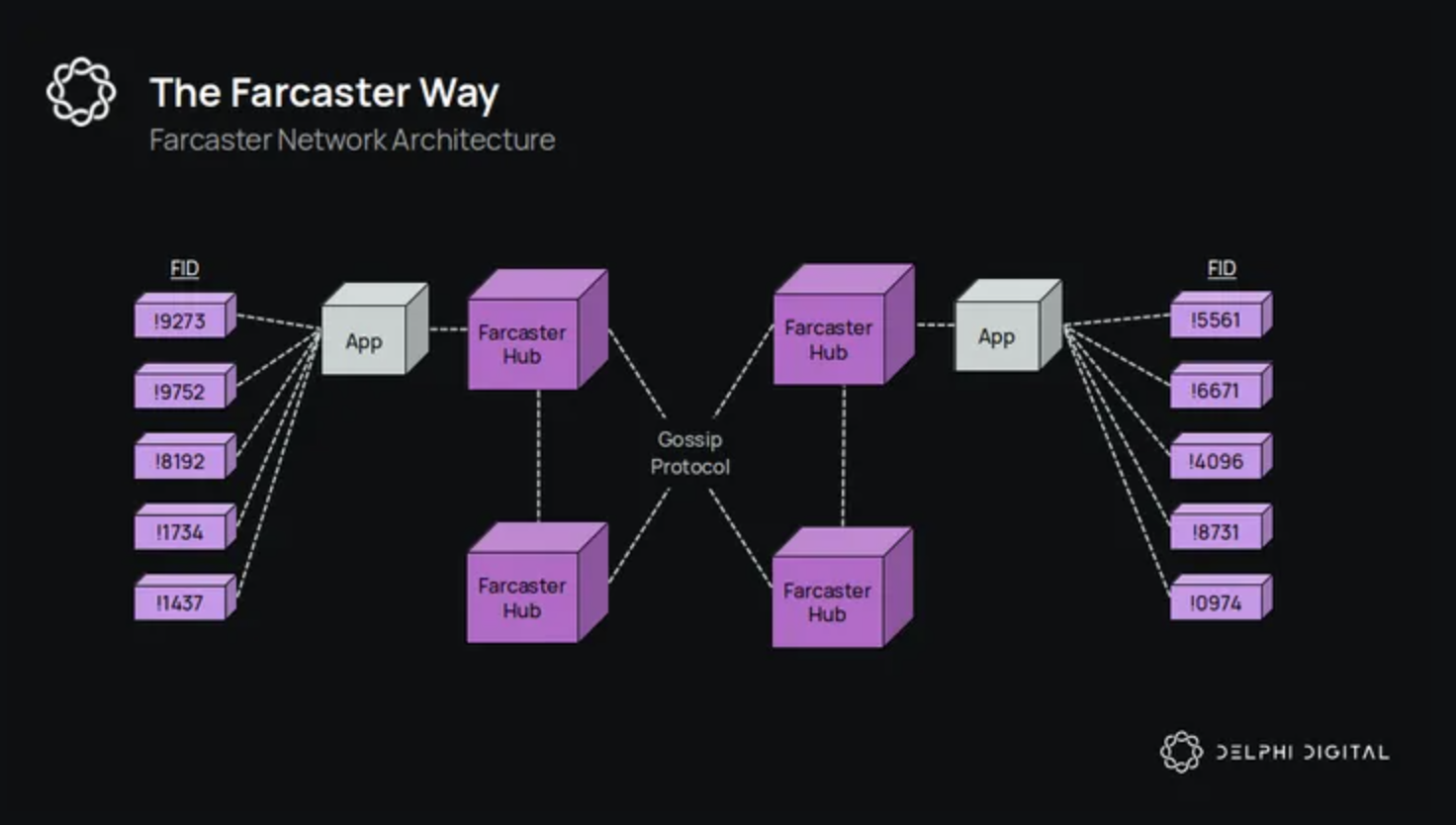
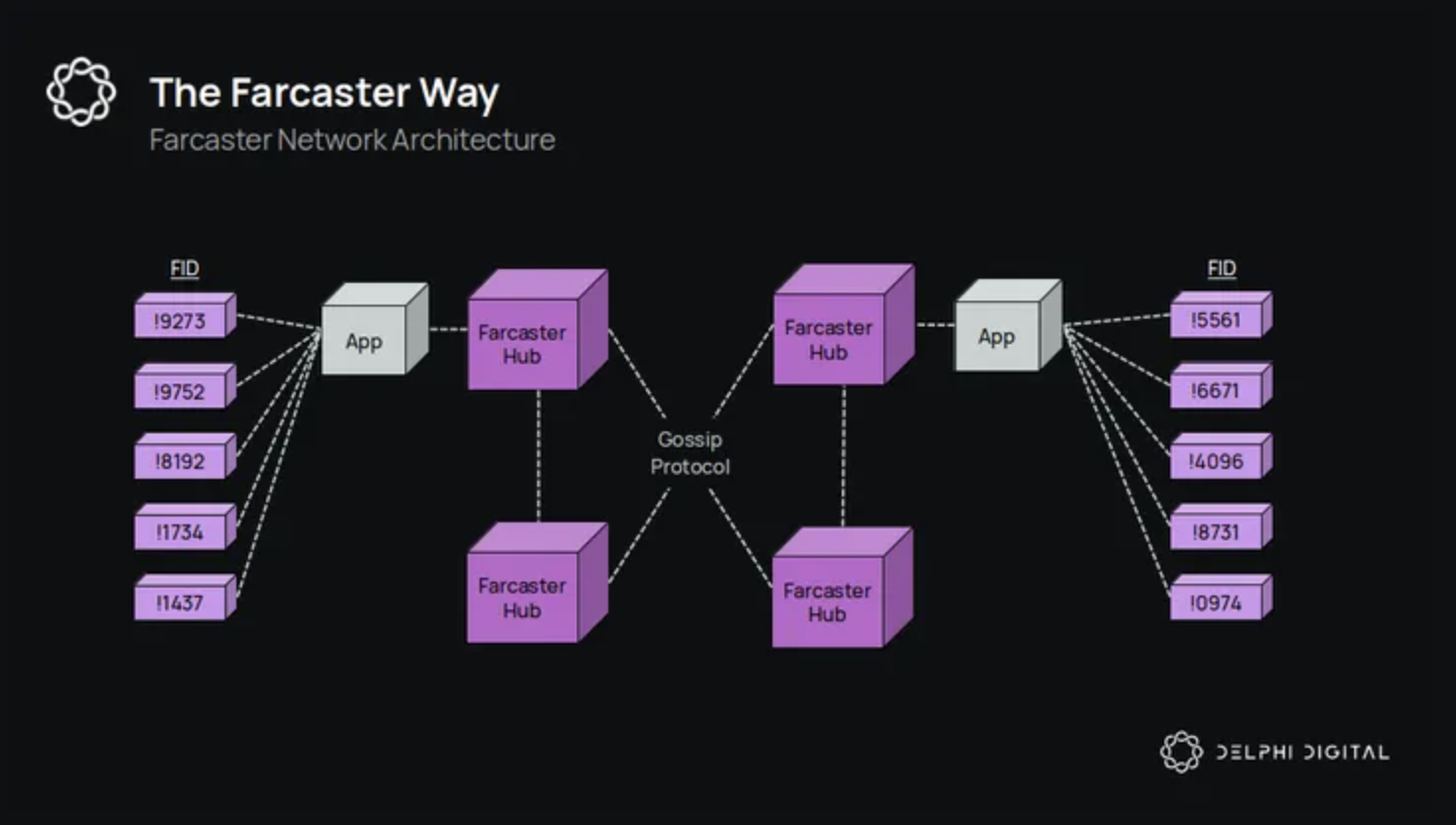
Farcaster is constructed atop Ethereum Layer 1 (L1) and Optimism, featuring a three-layer design:
- Identity Layer: Manages user identities with unique Farcaster IDs (fids) linked to Ethereum addresses.
- Data Layer (Hubs): Decentralized storage nodes ensure data consistency and availability using consensus mechanisms reminiscent of blockchain.
- Application Layer: Supports DApp development with integrated identity and storage primitives.
This modular structure allows Farcaster to deliver robust data propagation while maintaining high uptime through its offline Hubs. For developers, this means more predictable infrastructure performance and easier scaling as user activity grows. For more on how Farcaster’s architecture supports decentralized apps, see the analysis at Coinlive.
Lens Protocol, by contrast, operates on Polygon (Layer 2) and leans heavily into NFTs as core primitives. Every user’s profile is represented by a Profile NFT; social connections and content are also minted as NFTs. This approach emphasizes composability, portability, and creator ownership but introduces unique challenges around gas costs and transaction throughput, factors that developers must weigh when designing high-frequency or media-heavy applications.
Identity Management: FIDs vs. Profile NFTs
The way each protocol handles identity is foundational for both user experience and developer flexibility:
- Farcaster: Users receive a unique fid tied to their Ethereum address. Usernames are managed through ENS (. eth) or off-chain fnames. This dual system offers both on-chain verifiability and off-chain efficiency, developers can leverage ENS for integrations or rely on fnames for lightweight onboarding.
- Lens Protocol: Identity revolves around Profile NFTs, which control access to a user’s social graph and content. Handles (e. g. , @alice) are minted separately from Profile NFTs, allowing users to transfer or unlink their online persona without losing their social connections or content history.
This distinction has profound implications: Farcaster’s approach may appeal more to developers prioritizing seamless Ethereum integrations or those building apps where ENS compatibility is key. Lens’s NFT-centric model suits projects that want granular programmability around identity transferability or multi-profile experiences.
Data Storage and Availability: Hubs vs. Momoka L3
Farcaster‘s distributed Hubs act as decentralized storage points for all network data, using consensus-based validation for consistency. This ensures high availability, data remains accessible even if some nodes go offline, and supports rapid feature deployment thanks to its relatively centralized development team structure.
Lens Protocol, meanwhile, has innovated with Momoka, a bespoke Optimistic Layer 3 solution that processes certain transactions off-chain before settling them back onto Polygon L2. The result? Faster interactions at lower cost but with some trade-offs in finality guarantees compared to fully on-chain systems like Farcaster’s Hubs.
Pros & Cons: Hub-Based vs Momoka-Based Data Management
-

Farcaster Hubs: High Data Availability & SecurityFarcaster’s Hub-based architecture distributes data across decentralized nodes, ensuring robust data availability and security through a consensus mechanism similar to blockchain. This setup minimizes single points of failure and supports reliable data access for developers.
-
Farcaster Hubs: Greater Infrastructure OverheadOperating and maintaining decentralized Hubs can require significant resources and technical expertise. Developers may face higher setup and maintenance costs compared to lighter-weight solutions.
-
Lens Momoka: Fast & Cost-Efficient TransactionsLens Protocol’s Momoka (Optimistic L3) enables off-chain data processing, resulting in faster and cheaper user experiences. This is particularly beneficial for high-frequency social interactions and reduces on-chain congestion.
-

Lens Momoka: Lower On-Chain GuaranteesBy processing transactions off-chain, Momoka sacrifices some of the immutability and security guarantees provided by fully on-chain storage. This trade-off may concern developers building applications that require maximum trustlessness.
-
Farcaster Hubs: Consistent Data SynchronizationHubs use a consensus mechanism to maintain data consistency across nodes, reducing the risk of data conflicts or loss. This is crucial for applications where data integrity is paramount.
-

Lens Momoka: Enhanced User & Developer FlexibilityMomoka’s design allows developers to experiment with new features and users to interact with multiple clients without waiting for on-chain confirmation, fostering a more agile and diverse ecosystem.
The choice here impacts everything from app reliability during network congestion to how much control developers have over caching strategies or backup solutions.
Ecosystem Dynamics and Developer Experience
The ecosystem around each protocol shapes not just what you can build, but how quickly you can iterate:
- Farcaster: With roughly 80,000 daily active users (DAUs), it benefits from a single-team-driven roadmap enabling cohesive product experiences and tight integration between layers (Bitkraft VC analysis). This can be ideal for developers who value stability and rapid feature rollouts over maximal decentralization at the protocol level.
- Lens Protocol: DAUs range between 20,000-30,000 spread across multiple clients, a testament to its open API layer and community-driven ethos. Developers here enjoy greater creative freedom but may face more fragmentation in tooling or documentation as the ecosystem grows organically rather than under centralized guidance.
Monetization models are increasingly relevant as decentralized social networks mature. Farcaster has implemented a hybrid revenue approach: developers can set fees for Frames (interactive app modules), and users pay $0.01 per post. This model aligns incentives for both builders and the protocol, encouraging quality apps while deterring spam or low-value content. For developers, it means clear monetization pathways but also the need to design around microtransaction flows.
Lens Protocol also employs a hybrid revenue model, but its focus is on empowering creators and enabling programmable monetization through NFTs. Developers can build custom monetization logic into Profile NFTs, collect modules, or other primitives, supporting everything from tipping to subscription-based access. The flexibility is powerful but requires a deeper understanding of NFT standards and smart contract development.
User Growth, Community Dynamics, and Tradeoffs
The user base and community culture of each protocol should not be overlooked when making a technical choice:
Farcaster vs. Lens Protocol: Developer Ecosystem Approaches
-

Farcaster: Single-Team-Driven Growth — Farcaster’s core protocol and ecosystem are primarily developed and maintained by a single, dedicated team. This centralized approach enables rapid feature deployment and consistent user experiences across applications built on the protocol. The main Farcaster client, Warpcast, exemplifies this cohesive development, with approximately 80,000 daily active users (DAUs) as of September 2025.
-

Lens Protocol: Multi-Client Community Development — Lens Protocol fosters a community-driven ecosystem where multiple independent teams build diverse clients and applications using its open API. This decentralized approach encourages innovation and creator ownership, resulting in a network of apps with 20,000–30,000 DAUs distributed across various clients. Lens emphasizes programmable media and creator monetization through its NFT-based social graph.
Farcaster‘s 80,000 DAUs reflect rapid expansion driven by cohesive product vision and tight feedback loops between core developers and users. This environment fosters fast adoption of new features like Frames but can limit the diversity of client experiences in the short term.
Lens Protocol, with its 20,000-30,000 DAUs across multiple clients, demonstrates the power of open APIs and modularity. The diversity of apps built on Lens, ranging from creator-centric platforms to experimental social games, underscores its appeal to developers who want to differentiate their products or target niche communities.
Which Protocol Should You Build On?
The answer depends on your priorities as a developer:
- If you value rapid feature releases, integrated identity management (with ENS), predictable infrastructure performance, and are comfortable with some centralization in roadmap direction provides Farcaster is compelling.
- If your vision centers on creator empowerment, programmable NFTs, composability across multiple apps/clients, and you’re willing to navigate evolving standards provides Lens Protocol offers unmatched flexibility.
No matter your choice in the Farcaster vs Lens Protocol debate, both ecosystems are pushing decentralized social networks forward in unique ways. The best path may even involve building cross-protocol solutions that leverage the strengths of each, for example, using Farcaster’s robust identity layer alongside Lens’s NFT-powered content economy.
Which protocol would you choose for your next Web3 social dApp: Farcaster or Lens Protocol?
Both Farcaster and Lens Protocol offer unique approaches to decentralized social networking. Farcaster features a layered architecture with decentralized storage and rapid development, while Lens Protocol emphasizes on-chain social graphs via NFTs and a community-driven ecosystem. Which would you pick for building your next Web3 social dApp?
The decentralized social landscape is still young. The protocols you choose today will shape not just your application’s architecture but also your community’s experience for years to come.
If you’re interested in more technical deep-dives or want to see real-world code examples comparing these platforms side-by-side, check out our ongoing guides at FarcasterNews. com, and join the conversation as Web3 social continues to evolve.